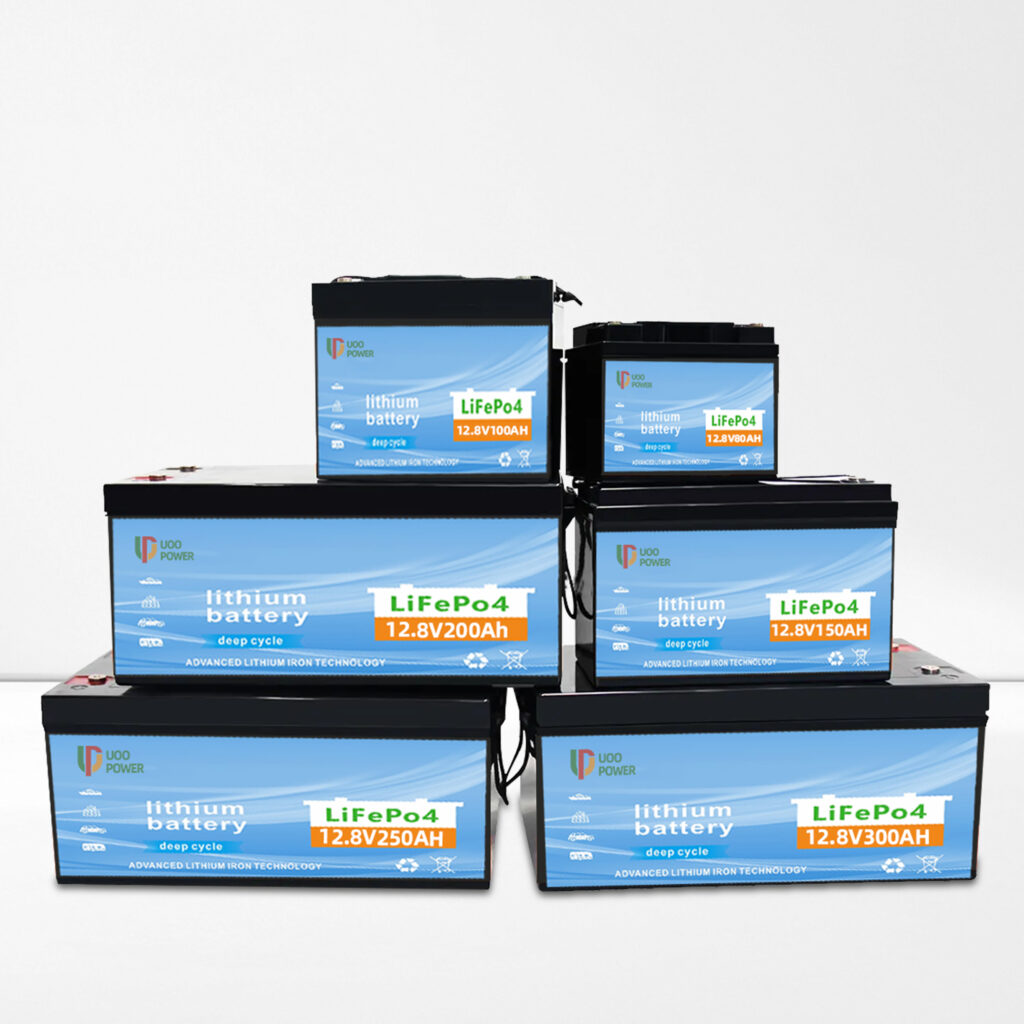

Lithium-ion battery is a kind of secondary battery (rechargeable battery), which mainly relies on the movement of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes to work. In the process of charging and discharging, Li+ goes back and forth between the two electrodes for embedding and de-embedding: when charging, Li+ is de-embedded from the positive electrode and embedded in the negative electrode through the electrolyte, and the negative electrode is in the state of lithium-rich; and the opposite is true when discharging.The application scenarios are as follows:
一 Generation Side
3. Providing fast-responding active power support for Automatic Generation Control (AGC) to stabilize grid frequency (Frequency Regulation – FR).
- Smoothing wind/solar power output fluctuations and enhancing renewable energy integration.
- Storing excess renewable energy generation and discharging it during peak demand or low generation periods (Energy Time-Shifting / Energy Arbitrage).
4. Serving as backup power for power plants or critical facilities, providing emergency power during main power outages.
二 Transmission & Distribution Side – Grid Side
5. Charging during off-peak grid demand and discharging during peak demand to reduce peak load stress and balance grid load (Peak Shaving / Valley Filling / Load Leveling / Energy Arbitrage).
6. Deferring or avoiding costly upgrades to transmission and distribution lines or transformers by deploying energy storage in areas with growing load demand (Transmission & Distribution Upgrade Deferral).
7. Providing or absorbing reactive power to help maintain stable voltage levels within acceptable limits at grid nodes (Voltage Support / VAR Support).
8. Providing initial power to start up a de-energized grid after a widespread blackout, assisting in grid restoration (Black Start Capability).
三 User Side / Behind-the-Meter – BTM
9. Helping commercial and industrial users reduce peak demand charges, arbitrage electricity prices between peak and off-peak periods, and provide backup power (Commercial & Industrial Energy Storage – Demand Charge Management / Price Arbitrage / Backup Power).
10. Coupled with rooftop solar PV systems to store solar energy for use at night or on cloudy days, reducing electricity bills; providing home backup power (Residential Energy Storage – Self-Consumption Optimization / Backup Power).
11. Serving as a core component of microgrids or off-grid systems, providing energy balancing, stabilizing voltage and frequency, and ensuring reliable power supply (Microgrid / Off-Grid System Support).
12. Deployed within EV charging stations to mitigate the impact of fast chargers on the distribution grid, reduce capacity upgrade costs, or participate in demand response programs (EV Charging Station Buffering / Grid Impact Mitigation).
四 Others
13. Serving as part of Uninterruptible Power Supply or backup power systems for data centers, providing high reliability assurance (Data Center Backup Power).
14. Mobile energy storage units or vehicles used for emergency response, disaster relief, and temporary power supply (Mobile Emergency Power Supply).
In practice, an energy storage project may serve multiple scenarios at the same time (e.g., a grid-side energy storage station may provide frequency regulation, peak shaving, and backup power services at the same time).

